A. U wave – Explanation
severely low. Low enough that management is likely going to be IV replacement in an area where there
is cardiac monitoring.
Thiazides such as bendroflumethiazide can increase potassium loss which results in hypokaleimia.
U waves are seen in hypokaleimia
The other answers are less likely:
J waves are usually observed in patients suffering from hypothermia.
Delta waves are seen in Wolff Parkinson White syndrome.
PR interval in hypokaleimia is prolonged.
QT interval remains the same in hypokaleimia although Q-T interval may be falsely seen as prolonged in
hypokalaemia. It is usually the U wave that is mistaken for the T wave. These are situations which may
falsely suggest a prolonged Q-T interval.
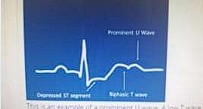
This is an example of a prominent U wave. A low T wave followed by a prominent U wave produces a
‘camel-hump’ effect
As hypokalaemia progresses to be more severe, the T wave decreases in amplitude and is flattened or
becomes inverted. The U wave becomes more prominent. This may falsely be seen as a prolongation of
the Q-T interval.
ECG features of hypokalaemiaz
- Prominent U waves
- Small or absent T waves
- Prolonged PR interval
- ST depression
Mnemonic: HypUkalaemia – U waves
