B. Naloxone – Explanation
A low respiratory rate, constricted pupils, semiconscious are features of opioid
poisoning. Naloxone is a specific antagonist for opioids and used especially in opioid
overdose to reverse coma and respiratory depression. When given intravenously, it can
begin to work within 2 minutes. The usual initial dose of naloxone for adults is 0.8 mg
intravenously (BNF says 0.4 mg initially then 0.8 mg). Dosingmaybe repeated at 2-3
minute intervals if there is minimal or no response. In known or suspected drug addicts
it is best to avoid reversing the opioid completely, so start with 0.1 mg of Naloxone
intravenously. This again can be repeated at 2-3 minutes intervals.
Naloxone has a much shorter duration of action compared to most opioids and so coma
and respiratory depression recur when naloxone wears off thus repeated dosing may be
required at a later time.
It is unlikely that the PLAB exam would ask you for the dose of Naloxone in the exam,
but it is worth remembering if you planto work in A&E in future.
PUPILLARY RESPONSES TO LIGHT
poisoning. Naloxone is a specific antagonist for opioids and used especially in opioid
overdose to reverse coma and respiratory depression. When given intravenously, it can
begin to work within 2 minutes. The usual initial dose of naloxone for adults is 0.8 mg
intravenously (BNF says 0.4 mg initially then 0.8 mg). Dosingmaybe repeated at 2-3
minute intervals if there is minimal or no response. In known or suspected drug addicts
it is best to avoid reversing the opioid completely, so start with 0.1 mg of Naloxone
intravenously. This again can be repeated at 2-3 minutes intervals.
Naloxone has a much shorter duration of action compared to most opioids and so coma
and respiratory depression recur when naloxone wears off thus repeated dosing may be
required at a later time.
It is unlikely that the PLAB exam would ask you for the dose of Naloxone in the exam,
but it is worth remembering if you planto work in A&E in future.
PUPILLARY RESPONSES TO LIGHT
An acutely widely dilated pupil unilaterally may be seen in unilateral space-occupying
lesions such as haematomas, tumours or abscesses.
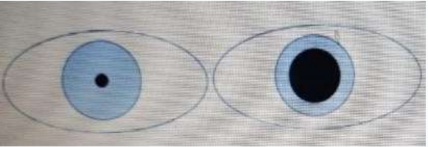
Bilateral abnormally constricted pupils may indicate opiate overdose or a
cerebrovascular accident affecting the brainstem

Bilaterally dilated pupils occur when there are sympathetic drugs that were taken e.g.
tricyclic antidepressant overdose.