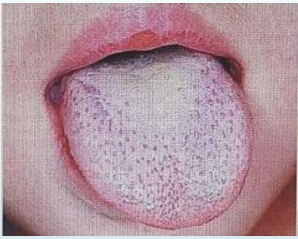
B. Scarlet fever – Explanation
coating of the tongue is an appearance of a white strawberry tongue. Usually, there is
also prominent red papillae seen. The rash described is characteristic of the rash of
scarlet fever.
The other options remain less likely
Roseola infantum (herpes 6 virus) may present with small (< 0.5 cm) blanching, rose-
pink rashes with a high fever. The rash also commonly affects the trunk which is seen
in this stem and it can present with a sore throat. However, they do not present with a
strawberry tongue. Also the most common age group that this disease occurs in is
around 6 months to 1 year. Note that roseola infantum, similar spots occur on soft
palate and uvula called Nagayama spots.
Rubella usually has a rash that starts behind the ears and spreads from there to the rest
of the face or body.
Measles usually present in a more unwell child with a fever more than 40 C. The red
spots begin on the face and behind the ears and spread over 24 to 36 hours covering
majority of the body except the soles and palms. The spots can initially be as big as 1
cm in diameter initially and often appear together.
SCARLET FEVER
Key points:
- Commonest in ages 2 to 8 years old
- Caused by group A streptococcus pyogenes
- Rash and fever are caused by toxins released by bacteria
- Diagnosis is clinical
- Presents with sore throat, fever (usually more than 38.3 C) and a rash
- Rash: Starts on torso 12 to 48 hours after fever and spreads to extremities, has a
coarse texture like sandpaper. - Other features
o Strawberry tongue
o Cervical lymphadenopathy
o Tonsils covered with pal exudates with red macules on palate (Forchhemier
spots) - Treatment is with penicillin V for 10 days
Picture of strawberry tongue